Diabetes mellitus is a group of endocrine diseases that develop as a result of chronic and chronic glucose absorption disorders.According to WHO estimates, about half a billion people worldwide suffer from this pathology.Correct and timely treatment of diabetes mellitus is very important for patients.It does not cause relief from the disease, but it allows a person to avoid severe complications and reduce symptoms, thereby ensuring a normal quality of life.
Cause
To put it simply, the cause of diabetes can be described as a decrease in the sensitivity of cells to the hormone insulin, or a violation of its secretion.
The pancreas synthesizes insulin, which maintains the desired level of sugar in the blood and ensures the supply of glucose to the cells of almost all body tissues.
In diabetes, metabolic processes are disrupted.Either the cells in the pancreas no longer produce enough insulin (type 1) or the body cannot use it properly (type 2).As a result, glucose, instead of entering the cells, accumulates in the blood and urine.Patients experience, respectively, hyperglycemia and glycosuria.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the multifactorial diseases.It can be triggered by:
- viral diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- physical inactivity;
- Excess weight, especially in the obesity stage;
- age-related changes;
- drink alcohol, overeat;
- uncontrolled use of drugs;
- hypertension;
- other endocrine pathologies;
- pancreatic injury;
- stress effect.
The possibility of developing this disease in the presence of one or more provoking factors depends on hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of diabetes
Symptoms of certain diseases include:
- frequent urination (polyuria).In diabetes mellitus, urine is released in large quantities, but without pain and mainly during the day;
- permanent thirst caused by dehydration;
- Increased appetite, which at the beginning of the disease can manifest itself in attacks.Patients are usually drawn to sweet foods that consist of simple carbohydrates;
- weight change.Due to excessive appetite, patients often lose weight due to increased protein and fat catabolism.
Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by other symptoms:
- decreased visual acuity;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- drowsiness (especially during the day), weakness, severe fatigue and increased sweating even with little effort;
- skin problems (itching, non-healing wounds, the appearance of dark bumps in certain areas);
- Dry mouth, gum inflammation, tooth decay.
In the first type, insulin deficiency develops quickly, and the listed symptoms increase rapidly and are difficult to ignore.In patients with type 2, the disease may be asymptomatic for a long time, and the signs that indicate it may not be very clear.Therefore, the second variant of the disease is often detected several years after its onset.
The patient may not show all the signs, but only 2-3 of them.In addition, the symptoms of hyperglycemia can disturb him only at a certain stage of the disease, and then the body seems to adapt to the increase in sugar, and this sensation disappears.Therefore, at the first signs of diabetes, it is important to carry out a special diagnosis.
Type of diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is not a single disease, but a group of pathological conditions.The international classification contains several types, but most patients are diagnosed with type 1 or 2 disease.Gestational diabetes is also common, which occurs during pregnancy and can threaten the health of women and children.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Type 1 diabetes begins when the pancreas stops producing insulin due to the destruction of beta cells.Because of this, an absolute lack of this hormone occurs in the body, carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted, and then other metabolic processes suffer.The disease usually begins before the age of 30, often in childhood or adolescence.
This type of disease is determined genetically, and the development of pathology occurs under the influence of external factors acting on the immune system.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed more often than type 1. The mechanism of occurrence is different: the pancreas still produces insulin, but glucose does not enter the cells due to impaired sensitivity to the hormone.Its amount in the blood always remains at a high level.This condition is called insulin resistance.
This disease usually develops in adults, usually after 40-45 years.The presence of excess weight is very important for the occurrence of the disease: according to statistics, it is typical for more than 80% of patients with this diagnosis.With the presence of this factor, hereditary tendencies are more likely to be realized, because due to excessive fat mass, a defect in the insulin receptor occurs.
In people who are not overweight, insulin resistance is caused by other causes, including endocrine and some other diseases.
Gestational Diabetes
This pathology occurs in pregnant women due to decreased glucose tolerance.This is an intermediate condition between prediabetes and diabetes, which usually disappears after delivery.It should be distinguished from the primary manifestations of type 1 or 2 encountered during pregnancy.
Women at risk:
- overweight;
- more than 30 years;
- Having a history of toxicosis and severe symptoms, chronic miscarriage, stillbirth, chronic malformations in children during previous pregnancies;
- suffering from cardiovascular and endocrine diseases.
Diabetes in pregnant women can start without these factors.
This pathology poses a threat to women and children, even leading to life-threatening conditions.Risks and possible complications can be prevented by keeping your sugar levels under control.
Risk factors
Many studies directly link the possibility of developing this disease to genetic predisposition.If one of the parents has type 1 diabetes, the chance of inheriting this disease is 5%;If both parents are sick, it increases to 20%.For a person whose parents have type 2 disease, the probability of getting this disease is about 80%, and in the presence of obesity it approaches 100%.
But even if you have a direct relative with diabetes, you can prevent the implementation of hereditary predisposition if you take risk factors and take preventive measures.
Visceral obesity is one of the main factors that cause the development of diabetes mellitus.Excess weight is caused by a poor diet with the use of simple carbohydrates, lack of physical activity, taking certain medications, and hormonal disorders (for example, excess androgens).According to international standards, hearing obesity is diagnosed when the waist circumference is more than 80 cm in women and more than 94 cm in men.
Other lifestyle factors include smoking, alcohol abuse and prolonged exposure to stress.
Other diseases
At risk are women with polycystic ovary syndrome, as well as people of both sexes with cardiovascular and endocrine diseases.
Age
All other things being equal, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases in people over the age of 45.
Diagnostic method
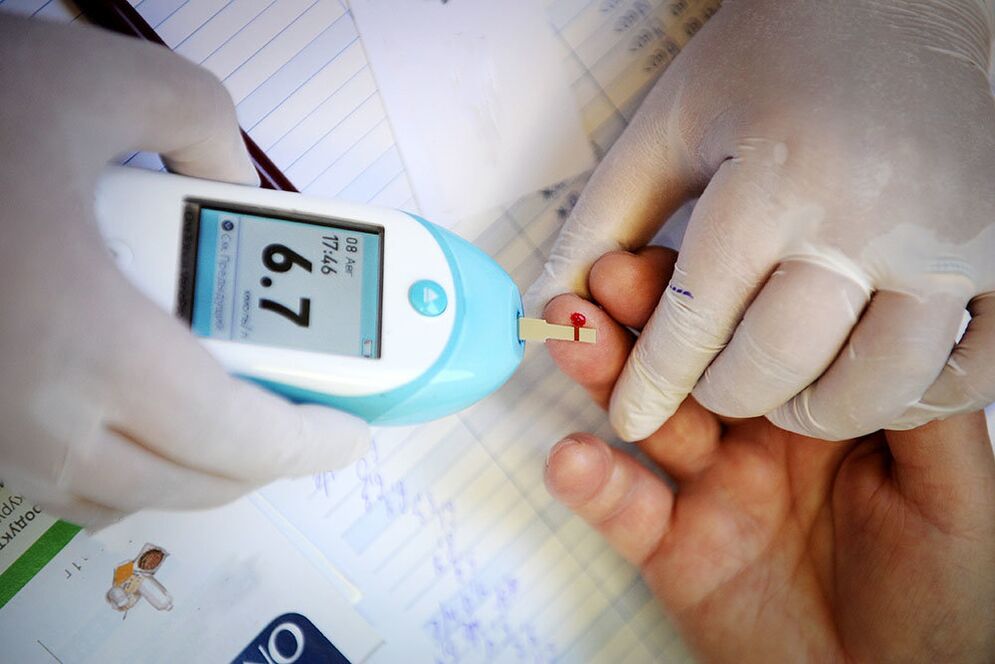
The most reliable way to diagnose diabetes is a laboratory test.The first thing that allows you to suspect the presence of a disease is that your blood sugar is higher than usual (on an empty stomach more than 6.1-7.0 mmol/L, and 2 hours after eating more than 11.1 mmol/L).If the result is in doubt, an additional glucose tolerance test is performed;It helps identify prediabetes.
During the examination, glycated hemoglobin, insulin resistance index, the presence of glucose in the urine are also checked, and tests for insulin and c-peptide are performed, which allow one to evaluate β-cell activity and the amount of insulin production.
To diagnose type 1 diabetes, especially in unusual cases, a blood test for antibodies to β cells is prescribed.
Patients can also be sent to specialists (cardiologists, ophthalmologists) for consultation to avoid complications.
It is better to undergo a full examination at a medical institution, where you can quickly get tests and get medical advice.Modern Medical Center has created conditions for fast and high-quality examination of patients.The technical equipment of the medical center allows you to carry out the necessary research, and the clinic uses experienced doctors who will prescribe treatment and clarify any questions that may arise.
Diabetes treatment
No method has yet been found to completely eliminate this disease.Treatment aims to stabilize the patient's condition, relieve symptoms and prevent complications.If all recommendations are followed, diabetic patients can minimize the impact of the disease on daily life.
Drug treatment may include insulin therapy or oral medications that lower blood sugar.Insulin is necessary for patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, because it solves the problem of compensation of carbohydrate metabolism and prevents the development of hypo- and hyperglycemia.In the second type, it is prescribed in case of ineffectiveness of other measures, as well as according to indications (for example, during pregnancy, significant weight loss, certain complications).
Antihyperglycemic drugs are prescribed to patients with the second type.This group includes products with different principles of action:
- increase insulin secretion;
- increase insulin sensitivity;
- reduce the absorption of carbohydrates and others;
They work in different ways, but ultimately help restore normal blood glucose levels.
Determining the treatment program, choosing drugs or their combination is the responsibility of the attending physician.You can get an appointment with an endocrinologist at the clinic with a referral from a local therapist or without a referral for a fee.You can make an appointment for a consultation online or by phone.
Other treatment methods are also used in combination with drugs:
- diet (diet for diabetes mellitus necessarily involves limiting carbohydrates),
- physical activity that can be carried out,
- Compensation for vitamin and micro deficiencies,
- Regular monitoring of sugar levels.
If complications or concomitant diseases occur, appropriate treatment is prescribed as well.Surgical methods (bariatrics) are also used in the treatment of diabetes when other measures are insufficient.
Possible complications
Impaired carbohydrate metabolism in diabetes mellitus affects the functioning of the entire body, but the disease has the most damaging effects on blood vessels.
Common diabetes complications are:
- retinal detachment;
- kidney failure;
- neuropathy;
- Atherosclerosis, which leads to many serious problems, including angina, heart attack and stroke.
This disease has a negative effect on the immune system, causing skin and joint pathology.
The most serious complication is diabetic coma.This condition can be caused by sugar levels that are too high or too low.In such cases, the patient needs immediate medical attention in intensive care.
Prevention of pathology
Measures to prevent diabetes mellitus partly coincide with general recommendations to maintain health and prevent disease.People with a genetic predisposition should watch it carefully:
- lead an active lifestyle and control weight;
- eat properly, reduce the consumption of fast carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets, etc.);
- giving bad habits (smoking, regular alcohol consumption);
- avoid unnecessary stress;
- After age 40, check your blood sugar levels every year.
In order not to miss the development of diabetes, to recognize it at an early stage and to help your body, it is important to monitor the warning signs and not hesitate to consult a doctor.